
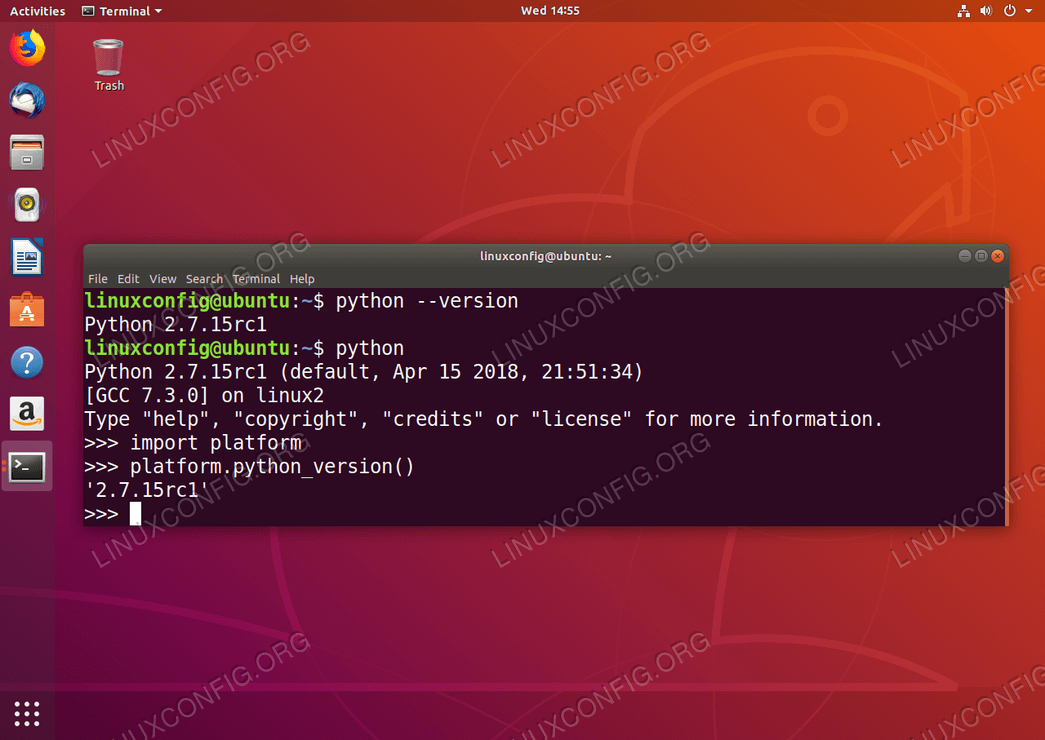
- #WINDOWS LINUX SUBSYSTEM UBUNTU INSTALL PYTHON 3.6 SOFTWARE#
- #WINDOWS LINUX SUBSYSTEM UBUNTU INSTALL PYTHON 3.6 LICENSE#
- #WINDOWS LINUX SUBSYSTEM UBUNTU INSTALL PYTHON 3.6 PLUS#
Among the more obscure distributions of SVR3.2 for the 386 were ESIX 3.2 by Everex and "System V, Release 3.2" sold by Intel themselves these two shipped "plain vanilla" AT&T's codebase. SCO UNIX was based upon SVR3.2, as was ISC 386/ix. The AT&T 3B2 became the official "porting base."

User interface improvements included the "layers" windowing system for the DMD 5620 graphics terminal, and the SVR3.2 curses libraries that offered eight or more color pairs and other at this time important features (forms, panels, menus, etc.). The final version was Release 3.2 in 1988, which added binary compatibility to Xenix on Intel platforms (see Intel Binary Compatibility Standard). SVR3 included STREAMS, Remote File Sharing (RFS), the File System Switch (FSS) virtual file system mechanism, a restricted form of shared libraries, and the Transport Layer Interface (TLI) network API. The AT&T 3B2 line of minicomputers was the porting base for SVR3ĪT&T's UNIX System Development Laboratory (USDL) was succeeded by AT&T Information Systems (ATTIS), which distributed UNIX System V, Release 3, in 1987.

Bach's book, The Design of the UNIX Operating System, is the definitive description of the SVR2 kernel. The first release of HP-UX was also an SVR2 derivative. Īpple Computer's A/UX operating system was initially based on this release.
#WINDOWS LINUX SUBSYSTEM UBUNTU INSTALL PYTHON 3.6 LICENSE#
A commercial source license was offered for $43,000, with three months of support, and a $16,000 price per additional CPU. The "porting base" is the so-called original version of a release, from which all porting efforts for other machines emanate.Įducational source licenses for SVR2 were offered by AT&T for US$800 for the first CPU, and $400 for each additional CPU. The concept of the "porting base" was formalized, and the DEC VAX-11/780 was chosen for this release. SVR2.4 added demand paging, copy-on-write, shared memory, and record and file locking. The DEC VAX-11/780 was the porting base for SVR2ĪT&T's UNIX Support Group (USG) transformed into the UNIX System Development Laboratory (USDL), which released System V Release 2 in 1984. Since the early 1990s, due to standardization efforts such as POSIX and the success of Linux, the division between System V and BSD has become less important. AT&T and Sun Microsystems worked together to merge System V with BSD-based SunOS to produce Solaris, one of the primary System V descendants still in use today. Throughout its development, though, System V was infused with features from BSD, while BSD variants such as DEC's Ultrix received System V features. While HP, IBM and others chose System V as the basis for their Unix offerings, other vendors such as Sun Microsystems and DEC extended BSD. The divide was roughly between longhairs and shorthairs programmers and technical people tended to line up with Berkeley and BSD, more business-oriented types with AT&T and System V. The dispute had several levels, some technical ( sockets vs. In fact, for years after divestiture the Unix community was preoccupied with the first phase of the Unix wars – an internal dispute, the rivalry between System V Unix and BSD Unix. Raymond summarizes the longstanding relationship and rivalry between System V and BSD during the early period: Historically, BSD was also commonly called "BSD Unix" or "Berkeley Unix".
#WINDOWS LINUX SUBSYSTEM UBUNTU INSTALL PYTHON 3.6 SOFTWARE#
In the 1980s and early-1990s, UNIX System V and the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) were the two major versions of UNIX.
#WINDOWS LINUX SUBSYSTEM UBUNTU INSTALL PYTHON 3.6 PLUS#
System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV.Īs of 2021, the AT&T-derived Unix market is divided between four System V variants: IBM's AIX, Hewlett Packard Enterprise's HP-UX and Oracle's Solaris, plus the free-software illumos forked from OpenSolaris. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V Release 4 (SVR4) was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as Unix System Unification, which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Unix System V (pronounced: "System Five") is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system.

HP 9000 workstation booting HP-UX, Hewlett-Packard's System V


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
